
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
Exercise 1. Expand on the statement
1. Better bend than break (Proverb).
2. A small debt produces a debtor; a large one an enemy. (Syrus).
3. There are some defeats more triumphant than victories. (Montaigne).
Exercise 2. Look through the text and find in it the words which you can understand without translation.
Exercise 3. Read the words with the suffixes – er. Try to guess the meaning which it gives:
1) risk-takers; 2) greater; 3) shareholder; 4) manager; 5) supplier; 6) customer, 7) wholesaler; 8) retailer; 9) manufacturer; 10) wider.
Exercise 4. Choose from the text all the predicates in the Passive Voice, translate them into Russian.
Exercise 5. Read the title of the text and try to predict the contents of the text.
Exercise 6. Read the text and find out:
1. What are the main variables which influence business operation?
2. How can the owners be characterized?
3. Where can the companies borrow funds?
4. What are the main groups of suppliers?
5. Who looks after employees’ interests?
6. What is consumer?
7. How are links between government and businesses realized?
8. What are the main characteristics of competitors?
Business environment
All types of businesses in Australia exist within an economic and social framework. This frame work includes a number of different variables which influence business operations.
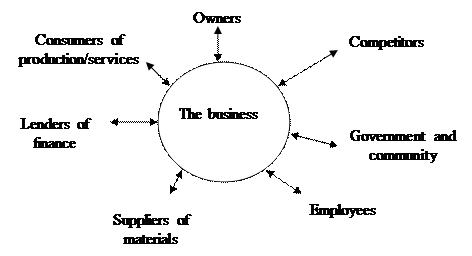 |
Look at these influences:
OWNERS
This group of people or organizations usually have the following characteristics:
· they initially fund and set the business up;
· they are risk-takers or entrepreneurs who believe that the prospects of future profits are greater than the risk of losses;
· they are sole proprietors, members of partnership, or shareholders in a company;
· they manage the enterprise themselves or employ managers to run the business for them.
LENDERS
Most businesses borrow funds from third parties such as banks and finance companies. Such arrangements are usually direct loans to the business, often secured by a mortgage. Banks also make overdraft facilities available to most businesses.
SUPPLIERS
Many types of businesses purchase goods from suppliers and resell them to their customers, either as they are, or after combining or altering them (i.e. acting as wholesalers/retailers, or manufacturers). Such purchases and sales are made on a credit or cash basis.
EMPLOYEES
Employees offer businesses necessary skills and expertise. They expect to be paid accordingly. Their interests, often looked after by trade unions or professional associations, increasingly cover wider areas than pure financial rewards. Hence the costs and benefits of employees have considerable effect on the business and require careful considerations by management.
Employees may also act as managers of the business. In this role they should act in its best interests. Financial information will be necessary to help them to do this.
GOVERNMENT AND
COMMUNITY
Businesses must have an awareness of legal and social requirements if they are to remain in existence. Taxation is a major factor. A business must act as a tax collector for government by withholding tax from employees, and, if set up as a company, must pay taxation itself. Federal, state, and local government bodies all have various regulations which business are expected to adhere to.
CONSUMERS
Consumers are the customers or clients of the business, those people or organizations who are prepared to buy, on cash or credit terms, the goods or services the business is offering.
COMPETITORS
Other organizations in the same industry selling similar products will have considerable effect on the ability of a business to survive. Competitors both in terms of price and quality must be taken into account by business managers. Gross profit margins (i.e. difference between cost and selling price of items) are influenced by competition in the market place.
Exercise 7. Read the text once again and define which variables belong to the external environment and which of them belong to the internal environment.
Exercise 8. Read the text once again, and express the contents of every passage in once sentence.
Exercise 9. Imagine that you are a businessman who is analyzing the environment of the organization at the meeting with potential partners. Make a presentation of your company business environment. Use in your presentation the following stages and phrases:
I stage: identifying yourself:
Let me introduce myself to you.
My name is …
I am from …
I have been working for this company for … years
II stage: preparing the audience:
I am going to divide my review into … areas.
I’d like to start with …
Then I am going to move on …
I am planning to finish with …
III stage: presenting the body of the material:
Firstly, secondly …
Talking about … it is worth mentioning …
Now, let’s move on to …
At this point we must consider …
Finally …
IV stage: closing:
Now, I’d like to summarize the main points again.
That’s all I have to say so far.
Thank you for your attention.
If there are some questions, I am ready to answer them.
Exercise 10. Write a short report to your top – manager with the analysis of your main competitor. Use the vocabulary, which is given in the passage of the text headlined “Competitors”.
Keys
Exercise 1.
Business, economic, social, operation, finance, materials, organizations, characteristics, risk, prospects, partnerships, company, managers, funds, banks, combining, overdraft, types, manufacturer, credit, basis, interests, professional, associations, effect, management, role, factor, collector, federal, local, clients, services.
Exercise 2.
1) doer of the action; 2) comparative degree of an adjective; 3) doer; 4) doer; 5) doer; 6) doer; 7) doer; 8) doer; 9) doer; 10) comparative degree of an adjective.
Exercise 3.
Are made; are prepared, must be taken; are influenced.
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 1599
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| MANAGEMENT | | | FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT |