
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Fig. 5. Immune responses against tuberculosis.Addition 3
LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS OF THE CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF THE PLAGUE, TULAREMIA Actuality. Causative agents, which you can learn in this topic, are related to highly pathogenic and particularly dangerous diseases for the humans and animals. Their biological properties are such that in the absence of the professional intervention when these diseases occur the epidemics of these diseases may be. The course of the disease is usually severe. Plague in the absence of medical intervention can lead to the death of the patient. Causative agents of these diseases are the basis of biological weapons developed earlier in some countries. Natural and geographical characteristics of Ukraine are such that there are conditions for human infection with any of these pathogens and epidemiological outbreaks of these diseases are missing only through the efforts of the health services. Primary objectives: to be able to conduct and evaluate the microbiological diagnosis of the plague and tularemia. QESTIONS FOR DISCASSION 1. Particularly dangerous infections are. 2. Biological properties of the F.tularensis causative agent of tularemia are. 3. Microbiological diagnosis of tularemia is. 4. Biological properties of Y.pestis the causative agent of the plague are. 5. Microbiological diagnosis of the plague is 6. Specific prevention of especially dangerous infections is. PROCEDURE OF PRACTICAL SESSION Task 1. Examine microscopically the smears from the patient's materials, fill in the protocol. Task 2. Study the growth of the Francisella tularensis on the solid media. Task 3. Study and write to the protocol information about immunobiological preparates for diagnostic, treatment and prophylaxis of the plague and tularemia. Task 4. Read the PHAT with the patient's pair sera and make the conclusion. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICAL WORK Task 1.
Francisella tularensis is very small Gram negative coccobacteria (the forms are intermediate between rhabdoid and orbed) with pronounced polymorphism. Certainly, their size is 0.2-0.7 microns.
Task 2.
Francisella tularensis forms on the solid media small white colonies.
Task 3. Tularemia diagnosticum is a frozen culture of the tularemia causative agent in the isotonic sodium chloride solution with formalin. Diagnosticum contains 25 billion microbial bodies in 1 ml. It can be used for: blood-drip reaction (used in undiluted form); expand agglutination test (EAT) to know the type of Widal reaction (in this case the diagnosticum is divorced by isotonic sodium chloride solution at 5 times). The EAT is often made with paired sera for detection the growth of antibody titer. Serum from the patient is diluted as 1:12.5 to 1:400. Reaction is considered positive if the titer is 1:100 and more. Pestilential erythrocytic antibody diagnosticum is the erythrocytes with adsorbed on them antibodies against the causative agent of plague. It is used to identify the causative agent in PHAT in rapid diagnosis. Pestilential bacteriophage contains a live bacteriophage. It is used for the phagolysis reaction to identify selected pure cultures in bacteriological method of diagnostics. Tularin is allergen. There are two types of tularin and under two input methods: tularin for dermal application and tularin for intradermal using. The first preparation is more convenient for mass examination for detection of the post-vaccinal immunity or immune layer among the population. Intradermal tularin is used for diagnosis of the acute diseases suspicious for tularemia. Various tularins contain various concentrations of allergens, so it is not advised to use dermal tularin for intradermal tests and vice versa. Plague live EV vaccin is dried culture of the Y.pestis from the live vaccine strain EV. It is used for prevention of the plague by epidemiological indications. Tularemia live vaccine includes the frozen living microorganisms from the vaccine strain of the tularemia cause. Vaccination are making for the people who live in the epizootic of the tularemia territory, and leaving such places. Vaccine is put on the skin once. In 1-2 weeks, the efficiency of the vaccination is verified by making the allergic skin test with tularin or serological reaction (AT and PHAT). In case of the negative result, make the revaccination. The vaccine provides immunity, which is kept to 5-15 years. Immunoglobulin antipestilential is gamma-globulin fraction from the blood serum of the hyper-immunization vaccine EV horses. It is used with preventive and curative purposes. Plague serum labeled FITS is used for direct reactions by Koons (IFT) when rapid diagnosis of the plague is necessary. Tularemia serum labeled FITS is obtained by classical way. It is used to identify the causative agent in blood smears and impressive smears from the animal organs that are contaminated by the material from the patient (bubo bioptate, sputum etc.). Task 4.
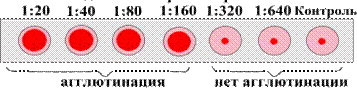
The serological method refers to additional methods of the plague diagnosis.
on the surface of rams of erythrocytes), which may indicate the causative agents of the disease (plague). Positive reaction appears as a turn umbrellas. Addition 1 Date: 2016-01-14; view: 1023
|

 Yersinia pestis is oval in shape, length to 2 mm, width – 0.3-0.7 microns, Gram negative. The bacteria are placed isolatedly. In preparations that are prepared from cultures growing on the solid media may be bacillary form, similar to E. coli. The bipolar painting (poles coated more intensely than the central part of cells) are seen better if the smears are stained methylene blue by Lefler method than the Gram method.
Yersinia pestis is oval in shape, length to 2 mm, width – 0.3-0.7 microns, Gram negative. The bacteria are placed isolatedly. In preparations that are prepared from cultures growing on the solid media may be bacillary form, similar to E. coli. The bipolar painting (poles coated more intensely than the central part of cells) are seen better if the smears are stained methylene blue by Lefler method than the Gram method.
