
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Flows of Funds through the Financial SystemLEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, you should be able to: · define the main types of financial institutions; · outline the basic components and structure of financial institutions industry; · define terminology related to financial institutions industry; · state the role of financial institutions industry.
Exercise 1.Answer the following questions. 1. What is a financial institution? 2. What are the examples of financial institutions? 3. What are the types of financial institutions? Exercise 2. The financial system matches savers and borrowers through two channels: (1) financial intermediaries and (2) financial markets. These two channels are distinguished by how funds flow from savers, or lenders, to borrowers and by the financial institutions involved. a) Comment on the following scheme using the word-combinations from the table below.
Flows of Funds through the Financial System
b) In order to clear up your knowledge of indirect and direct finance choose the correct alternatives. In indirect finance (the route at the top of the scheme), the flow is indirect because the funds the financial intermediaries lend/ borrow you come from people who have put money in checking or savings deposits in the bank or other financial intermediary/ instrument; in that sense, they are not lending their own property/ funds directly to you. In direct finance (the route at the bottom of scheme), borrowers lend/ borrow funds directly from lenders in financial markets/ intermediaries by selling them securities (also called financial intermediaries/ instruments), which are claims1 on the borrower’s future income or assets. Securities are assets/ liabilitiesfor the person who buys them but liabilities/ assets (IOUs or debts) for the individual or firm that sells (issues) them. 1 – áîðãîâå çîáîâ’ÿçàííÿ c) Define which type of finance (direct or indirect) each of the following examples illustrates. 1. If General Motors needs to borrow funds to pay for a new factory to manufacture computerized cars, it might borrow the funds a saver by selling the saver a bond, a debt security that promises to make payments periodically for a specified period of time. 2. Mr. Franklin has saved some funds but he doesn’t have the whole needful sum. So he decided to get a loan from a bank to buy a car. 3. In order to possess some long-term assets Mrs. Watson decided to buy stock that a firm has just issued.
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 5033
|

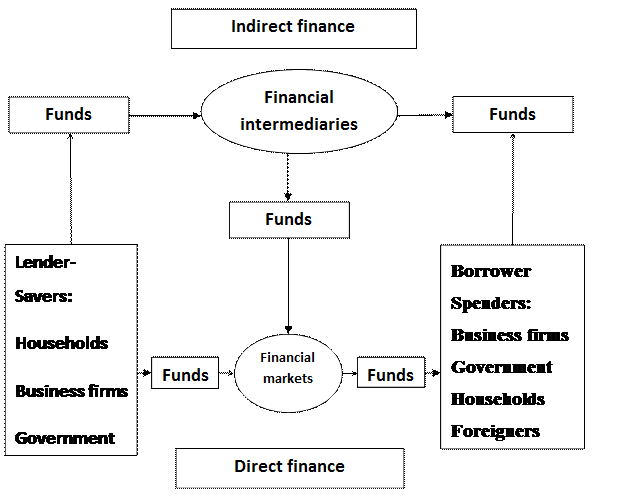
 d) Give your own examples that illustrate direct and indirect finance.
d) Give your own examples that illustrate direct and indirect finance.