
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Quantity Average Average Marginal
of Output Variable Cost Total Cost Cost
1 50 250 50
2 45 145 40
3 41.7 108.4 35
4 40 90 35
5 40 80 40
6 40.8 74.1 45
7 42.1 70.7 50
8 44.3 69.3 60
53. Refer to Figure 14. The average fixed cost of producing 4 units of output is:
A. 35
B. 40
C. 50
D. 90
E. 200
54. Refer to Figure 14. If product price is $47.00, to maximize profits this firm will produce:
A. zero, the firm will lose money by producing any level of output
B. zero in the short run, but 6 in the long run
C. zero in the long run, but 6 in the short run
D. 1 in the short run, but 7 in the long run
E. 7 in the long run, but 1 in the short run
55. Refer to Figure 14. If fixed costs increase by 100, what will happen to each of the following?
Average Average Marginal
Variable Cost Total Cost Cost
A. increase increase increase
B. increase increase no change
C. no change increase increase
D. no change increase no change
E. no change no change increase
56. A price discriminating monopolist would differ from a non-price discriminating monopolist in which of the following ways?
Profit Consumer surplus
A. higher w/ price discrimination higher w/ price discrimination
B. higher w/ price discrimination lower w/ price discrimination
C. lower w/ price discrimination lower w/ price discrimination
D. lower w/ price discrimination higher w/ price discrimination
E. the same with both the same with both
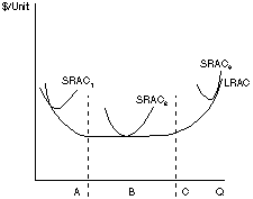
Figure 15
57. Figure 15 shows short run and long run average total cost curves. Section A, B, and C respectively demonstrate:
A. economies of scale, diseconomies of scale, constant returns to scale
B. economies of scale, constant returns to scale, diseconomies of scale
C. diseconomies of scale, constant returns to scale, economies of scale
D. diseconomies of scale, economies of scale, constant returns to scale
E. constant returns to scale, economies of scale, diseconomies of scale
58. Which of the following correctly describes a perfectly competitive firmís short run supply curve?
A. marginal cost curve
B. rising portion of the marginal cost curve
C. rising portion of the marginal cost curve above equilibrium
D. rising portion of the marginal cost curve above average variable cost
E. rising portion of the marginal cost curve above average total cost
59. Under conditions of imperfect competition which of the following is true for a profit maximizing firm?
A. AR > MR
B. MR > AR
C. AR > P
D. AR < P
E. AR = MR
60. Based on the information in the following table, what is the only answer set that could be answered zero, and yes?
Long Run Profits Efficient Producer
Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
Pure Monopoly
A. Perfect competition
B. Monopolistic competition
C. Oligopoly
D. Pure monopoly
E. All of the above
Answers
- C
- C
- C
- B
- B
- A
- B
- C
- B
- C
- C
- D
- A
- C
- D
- C
- B
- D
- A
- D
- D
- B
- B
- E
- B
- B
- B
- C
- D
- B
- C
- B
- D
- B
- A
- D
- C
- C
- E
- A
- A
- C
- C
- B
- B
- D
- B
- C
- C
- A
- B
- A
- C
- C
- D
- B
- B
- D
- A
- A
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 1181
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Price of Good A Income of Good A Quantity demanded | | | “Ň —“ Ń Mining and Geological Higher Education in Russia |