
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Energy is the ability to do work or make a change.4. A body which is moving has kinetic energy. 5. Raise a book & put it on a high shelf. Your energy is stored in the book. The stored energy is potential energy.
Mechanical energy = potential energy only. Mechanical energy of the ball at B = Mechanical energy only.
Potential energy increases when the objects weight or height increase. Potential energy = weight x height. Example: compare the potential energy of 2 balls, the weight of each is 1 Newton & the first is placed at a height of 1m & the 2nd is placed at a height of 2 m.
Solution: Potential energy (1) = 1 Newton x 1 m = 1 Joule Potential energy (2) = 1 Newton x 2 m = 2 Joules Potential energy of the 2nd object is double the potential energy of the 1st object. Kinetic energy increases if the mass or the speed of the moving object increase.
A solved example: Calculate the kinetic energy of a ball that has a mass =0.5 kg & moves with a speed 3 m/s. Solution: Kinetic energy = ½ x 0.5 x (3)2 = 2.25 Joules.
I. Choose the correct answer: 1. An object of 20 N weight is placed on a shelf of height 5 m. its potential energy = .J (50 100 150) 2. A truck & a car move with the same speed. The car has kinetic energy than/ as truck. (less more the same) 3. The ..energy of water at the top of waterfalls is maximum. (kinetic potential mechanical) 4. (doesnt change increases decreases) 5. An object is thrown upwards, therefore its velocity ... (increases decreases doesnt change)
II. Solve the following problems: 1. Calculate the mechanical energy of a book whose weight = 10 Newton & is placed on a shelf 3m high.
2. Calculate the mechanical energy of a ball of weight 3 Newton , its mass = 0.3 kg , its thrown up with speed 3 m/s to a height 4m.
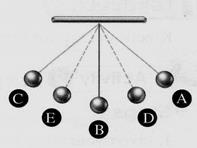
A pendulum is a ball tied with a string & fixed at a point. When the ball is pushed, it moves to the right & then back to the beginning point, then to the left.
A B
At points A&B , the potential energy of the pendulum is maximum. As it moves away from point A, its energy is changed to kinetic energy. The mechanical energy of the pendulum is the same at each point.
Forms of energy:
Activity 1: Simple cell 1. In a glass beaker, put 2 metal plates separately 2. Fill half the beaker with diluted acid. 3. Connect the 2 plates externally with an electric current. 4. Put a voltammeter in the circuit to measure the electric current. Ø Observation : The pointer of the voltammeter moves to indicate the electric current is passing through the circuit. Ø Conclusion: Chemical energy in the simple cell is transformed into electric energy.
Activity 2: Prepare an electric circuit like the one in the figure, close the circuit using the switch , open the circuit using the switch. Ø Observation : The bulb light up when the circuit is closed. The bulb is turned off when the circuit is open & electricity isnt passing in the circuit. Ø Conclusion: In the electric bulb (lamp) electric energy is converted into light energy.
Energy is transformed from one form to another as in the following table.
Modern technology has many harms, some are mentioned in the following table.
Nuclear weapons
I. Fill in the blanks: 1.
2.
II.
 Choose the correct answer: Choose the correct answer:
1. The mechanical energy of the ball at position A = (kinetic energy only potential energy only kinetic energy x potential energy) 2. The work done to raise a book to a high shelf is stored in the book as energy. (heat potential chemical) 3. The dynamo produces energy. (chemical kinetic electric) III. Write the scientific term:
IV. Explain some of the harms of using nuclear weapons in wars.
V. Use the opposite figure to fill in the blanks. 1. The kinetic energy = the potential energy at position(s) . 2. The kinetic energy is maximum at position(s) . 3. The potential energy is maximum at
1. Ice cubes are placed in a glass of juice to make the juice cooler.
2. Rub your hands together & notice that they become hot. As the speed of rubbing increases so does the heat energy. 3. How is heat transferred through different mediums ? 1. Through solids: Ø 2. Put some tea dust in a beaker that contains water. Heat the beaker with Bunzen burner. Observe: how tea dust moves up then falls down in circles. Ø Conclusion:when heated, the molecules of liquids move up & are replaced by cooler water, falling down. This way of heat transfer is called convection. 3. Heat is transferred from the Sun through space to the Earth by radiation.
Heaters are usually placed on the floor because the density of hot air is low, therefore hot air rises up. The heat is distributed in the room by convection. Date: 2015-12-24; view: 1017
|


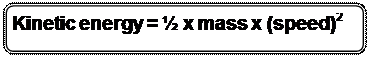 The following rule calculates kinetic energy .
The following rule calculates kinetic energy .

 The kinetic energy of a falling ball
gradually.
The kinetic energy of a falling ball
gradually.



 Sound
Sound


 Television
Television
 Cellular phone (mobile)
Cellular phone (mobile)
 Sewing machine
Sewing machine
 Alarm clock
Alarm clock



 When the cyclist presses the brakes to stop the bicycle, the tyres rub against the ground & become heated friction produced heat energy.
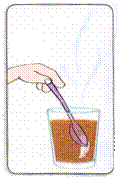
When the cyclist presses the brakes to stop the bicycle, the tyres rub against the ground & become heated friction produced heat energy. Leave a metal spoon in a cup of hot tea. Touch the end of the spoon outside the cup. It feels hot because heat was transferred in the spoon by conduction.
Leave a metal spoon in a cup of hot tea. Touch the end of the spoon outside the cup. It feels hot because heat was transferred in the spoon by conduction.

 Air conditioners are placed in a high place in the room because cold air is denser than warmer air, therefore cold air moves downwards. Convection distributes cold air in the room.
Air conditioners are placed in a high place in the room because cold air is denser than warmer air, therefore cold air moves downwards. Convection distributes cold air in the room.