CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
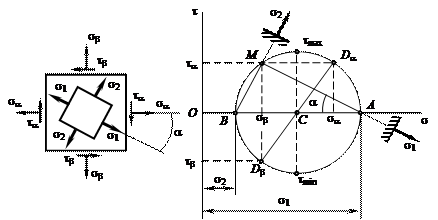
Task 2. Analysis of the stress state in the pointThe element is selected in the neighbouring area of the certain point of the stressed body. Study the stress state and deformations of the element. Take the values of stresses from table 3 and element from fig. 2. Order of work 1. Determine the principal stresses. 2. Determine the position of principal areas and draw the lines of principal stresses. 3. Determine the biggest value of shear stresses and position of the areas under their action. 4. Calculate principal strains and unit volume change. 5. Determine the unit potential energy of strain. 6. Check up strength of the material. 7. Construct the Mohr’s circle of stress (fig. 3).
table 3
Fig.2. (see also p.9)
Fig.2. Ending
Fig. 3
1. External forces (loads). 2. Method of sections. Simple types of deformations. 3. Determination of internal forces, longitudinal forces diagram in tension and compression. 4. Determination of stresses. Normal stress diagram in tension and compression 5. Hooke’s law in tension and compression. Determination of deformations. 6. Hooke’s law in tension and compression Modulus of longitudinal elasticity and factor of lateral strain (Poisson's ratio). 7. Experimental study of the properties of materials. Tensile test diagram for a low-carbon steel specimen. 8. Experimental study of the properties of materials. Characteristics of strength and ductility. 9. Condition of strength in tension (compression). Choice of allowable stresses. 10. Basic types of problems in tension and compression. 11. Work of forces in tension (compression). Potential energy of strain. 12. Elongation of stepwise and constant cross section bars in tension (compression). 13. Elongation of the constant cross section bars under its own weight. 14. Statically indeterminate problems in tension and compression. 15. Thermal stresses in tension and compression. 16. Elongation of stepwise and constant cross section bars under its own weight. 17. Principal stresses and principal areas. Types the state of stress. 18. Stresses on inclined sections under tension (compression) in one direction (uniaxial state of stress). 19. Determination of stresses on inclined sections under tension (compression) in two direction. 20. Determination of principal stresses and position of principal areas. 21. Graphical method of the stress determination. Mohr’s circle of stress. 22. Relation between strain and stresses in plane and three-dimensional states of stress (generalised Hooke’s law). 23. Check the material strength in three-dimensional states of stress. Strength theories.
Date: 2015-12-24; view: 1011
|