
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
AMERICA IN THE PACIFIC
A firm must become involved in the channel design process when it is considering entering the market with a new product or when existing supply chains are falling short of performance objectives.
The design process consists of the following steps:
1. Establish objectives.
2. Formulate a strategy.
3. Determine structure alternatives.
4. Evaluate structure alternatives.
5. Select structure.
6. Determine alternatives for individual channel members.
7. Evaluate and select individual members.
8. Measure and evaluate channel pertormance.
9. Evaluate alternatives when performance objectives are not met, or attractive new options become available.
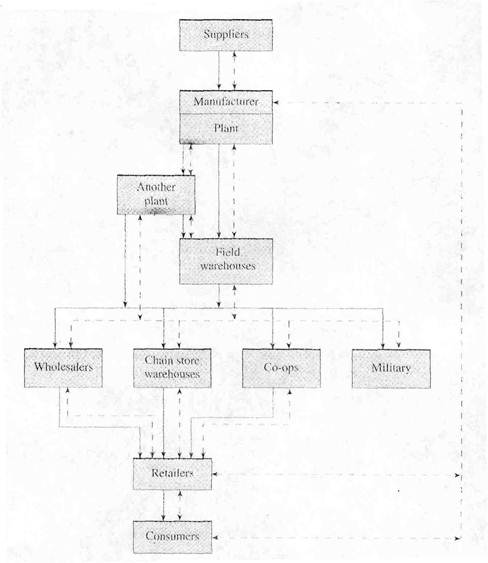
Figure 4-1
4.7. Types of distribution
Three types of distribution can be used to make product available to consumers:
(1)intensive distribution, (2) selective distribution and (3) exclusive distribution.
In intensive distribution, the product is sold to as many appropriate retailers or wholesalers as possible. Intensive distribution is appropriate for products such as chewing gum, candy bars, soft drinks, bread, film, and cigarettes where the primary factor influencing the purchase decision is convenience. Industrial products that may require intensive distribution include pencils, paperclips, transparent tape, file folders, typing paper, transparency masters, screws, and nails.
In selective distribution, the number of outlets that may carry a product is limited, but not to the extent of exclusive dealing. By carefully selecting wholesalers or retailers, the manufacturer can concentrate on potentially profitable accounts and develop solid working relationships to ensure that the product is properly merchandised. The producer also may restrict the number of retail outlets if the product requires specialized servicing or sales support. Selective distribution may be used for product categories such as clothing, appliances, televisions, stereo equipment, home furnishings, and sports equipment.
When a single outlet is given an exclusive franchise to sell the product in a geographic area, the arrangement is referred to as exclusive distribution. Products such as specially automobiles, some major appliances, certain brands of furniture, and lines of clothing that enjoy a high degree of brand loyally are likely to be distributed on an exclusive basis. This is particularly true if the consumer is willing to overcome the inconvenience of traveling some distance to obtain the product. Usually, exclusive distribution is undertaken when the manufacturer desires more aggressive selling on the part of the wholesaler or retailer, or when channel control is important, exclusive distribution may enhance the product's image and enable the firm to charge higher retail prices.
Sometimes manufacturers use multiple brands in order to offer exclusive distribution to more than one retailer or distributor. Exclusive distribution occurs more frequently at the wholesale level than at the retail level. In general, exclusive distribution lends itself to direct channels (manufacturer to retailer). Intensive distribution is more likely to involve indirect channels with two or more intermediaries.
4.8. Product characteristics
Nine product characteristics should be analyzed by the channel designer:
· Product value.
· Technicality of the product.
· Degree of market acceptance.
· Degree of substitutability.
· Product bulk.
· Product perishability.
· Degree of market concentration.
· Seasonality.
· Width and depth of the product line.
4.9. Processes of integrated supply chain management
3M managers identified seven key processes requiring analysis which support the integrated SCM approach. These key processes are:
· Customer relationship management.
· Customer service management.
· Demand management.
· Order fulfillment.
· Manufacturing flow management.
· Procurement.
· Product development and commercialization.
· Returns channel process.
AMERICA IN THE PACIFIC
For many years Japan had kept itself apart from the rest of the world. Japanese rulers had allowed almost no trade with Europe and America. But in 1854 President Millard Fillmore sent Commodore Matthew Perry to Japan, and a treaty of trade was signed which gave great opportunities for both countries.
In 1867 the Senate approved buying Alaska from Russia. The price was a little over seven million dollars. Alaska became an American territory. A huge area had been added to the United States. Fishing along the Alaska coast was already an important business. Alaska proved to be a rich storehouse of other nature resources. These included timber, furs, gold, and copper. Many years later huge amounts of oil were discovered off Alaska's northern coast. When Alaska became a state in 1959, people in Anchorage pinned an extra star on a 48-star flag.
By the late 1800's Americans were taking an even greater interest in distant lands looking for new places as markets for their goods and new sources of raw materials. One of such places was Hawaii. The Americans living in Hawaii had grown powerful and by 1893 they wanted to govern the islands themselves. They took away the queen's power and set up a republic. Five years later Hawaii became a United States territory.
In 1899 the United States and Germany agreed to divide the Samoan islands between them. In this way the U.S. got another Pacific possession - it became known as American Samoa.
1. Who opened up trade between the United States and Japan?
2. Why was Alaska a big purchase for the United States?
3. How did Hawaii become an American possession?
4. How was American Samoa acquired?
THE END OF THE CENTURY WAR WITH SPAIN
From the days of Christopher Columbus, Cuba had been a colony of Spain. In the 1860's the Cuban people began trying to break away from Spanish rule. In the 1890's Cuban guerrillas started a rebellion against the Spanish government. American companies had large sugar plantations on that island. William McKinley was President of the United States in 1898, when on April 25, the Spanish-American War started after the explosion of the American battleship called the Maine. The only hard fighting of the war took place near the city of Santiago, Cuba.
Theodore Roosevelt was an official in the Department of the Navy when the war started. He quit his job, organized an army unit called the Rough Riders and led it and a unit of black American cavalry in the attack on a place called San Juan Hill. The Spanish surrendered in Cuba. But the main Spanish fleet was protecting the Philippines far across the Pacific. The American fleet commanded by Commodore George Dewey destroyed the Spanish fleet.
After the United States took over, Philippine guerillas continued to fight for independence; they resisted American control for three years before giving up. Many years later, in 1946, the Philippines became an independent republic.
After the war Cuba became a republic, but the United States did, however, keep the right to take a hand in Cuban affairs and the American navy kept a base on the island.
Puerto Rico had not been a battleground in the Spanish-American War, but under the peace terms, however, Spain turned the island over to the United States. Puerto Rico was governed by the United States until 1952. Guam is still a United States territory. Its people are citizens of America, and elect their own governor.
1. What were the interests of the United States in Cuba and other Spanish territories in the Caribbean and in the Pacific?
2. What happened to the Spanish colonies? What possessions did the United States get as a result of the war?
Date: 2015-01-02; view: 1025
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Channel Design | | | THE 20TH CENTURY |