
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Chemical Combination
- Chemical reaction:is a process by which chemical bonds between reactants are broken and new bonds between products are formed.
Chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, coordinate, hydrogen and metallic bond.
Ionic bond: It is an electrostatic attraction forces between +ve ion of metal element and -ve ion of non-metal element. It has no. materialistic existence.

It is formed when the difference in electronegativity between the two reactants atoms is more than 1.7.
- The difference in electro negativity increases as the distance between the two elements in the same period increases and so the ionic properties, the melting point, the boiling point and the electrical conductivity increase.
Covalent bond: It arises mostly between atoms of non-metal elements.
Types of covalent bonds:
- A pure covalent bond between atoms of two elements equal in electronegativity.
ex: The bond Cl2 molecule:
- A polar covlent bond between atoms of difference in electronegativity less than 1.7. The atom of higher electron negativity has partial -ve charge  , and the atom of lower electronegativity carry partial +ve charge
, and the atom of lower electronegativity carry partial +ve charge  .
.
Octet rule (Electronic of valency theory):
All elements except hydrogen , Lithium and Beryllium tend to reach the Octet structure.
Disadvantages of Octet rule:
It can not explain the binding in many molecules in which the number of electrons around the central atom is more or less than eight.
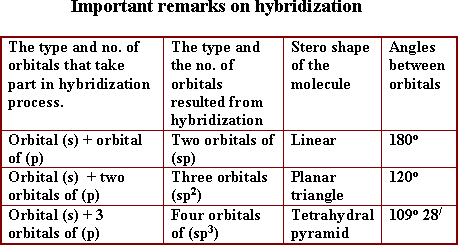
It is not sufficient to explain the properties of molecules such as the stereostructure and the angles between bonds:
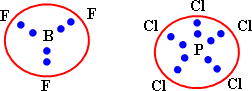
The valence bond theory:
It considers the covalent bond in the molecule is formed as a result of the overlap of half filled atomic orbital of one atom with another half filled atomic orbital of another.
Hybridization:
It is the combination between two different orbitals or more in the same atom to form new orbitals which are equivalent in shape and energy. The difference in energy between hybride orbitals is very small value. Ex: (2s, 2p) . The number of hybride orbitals = the number of pure orbitals
- Hybridized orbitals are more protrude to the outside than pure ones.
The molecular orbital theory:
- It considers the molecule as one unit or a big atom with multinuclei in which all the atomic orbital of the combined atoms are mixed forming molecular orbital.
- Sigma bond  is a covalent chemical bond formed from overlaping of atomic orbital (head by head) when they are alone one line.
is a covalent chemical bond formed from overlaping of atomic orbital (head by head) when they are alone one line.
- Pi bond  a chemical bond formed from overlaping of two atomic orbtials side by side when they are parallel.
a chemical bond formed from overlaping of two atomic orbtials side by side when they are parallel.
- Methane molecule (CH4) tetra hydral pyramid in shape, the hybridization of (sp3) type, all bonds are sigma type, and the angles between orbitals are  .
.
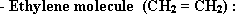
It takes the planar triangle shape, the hybridization of (sp2) type. Two covalent bonds exist between the two carbon atoms, one of them is sigma and the other is pi type. The angles between orbitals equal (120o).
Coordinate bond:
It is formed between two atoms, one of them (donar atom) having alone pair of electrons donated to the other atom (acceptor atom) having a vacant orbital.
- Hydronium ion  has two covalent bonds and coordinate bond
has two covalent bonds and coordinate bond
QUESTION and ANSWER 1:
I. Choose the correct answer from those between brackets:
1- The bond in NaCl molecule is .............. bond.
(a- ionic, b- convalent, c- coordinate, d-metallic)
1-a: ionic
2- The bond in  molecule is .............. bond.
molecule is .............. bond.
(a- ionic, b-hydrogen, c-pure covalent, d-polar covalent)
2-c: pure covalent
3- The bond in HCl molecule is ............... bond.
((a-ionic , b- pure covalent, c- polar covalent, d- coordinate)
3-c: polar covalent
4- In AgCl , the covalent bond character is ……….. Than ionic bond character.
4- greater
5- The bond in between two elements, their atomic Numbers 8, 12 when froming a compound is ................. bond.
(a- ionic, b-covalent, c-coordinate, d-metallic.
5-a: ionic
6- The bond between two atoms of an element (  ) when forming a molecule (
) when forming a molecule (  ) is .............. bond.
) is .............. bond.
(a-ionic, b- pure covalent, c-polar covalent , d- coordinate)
6-b: pure covalent
7- The bond between two elements  when forming a compound (YZ) is ............ bond.
when forming a compound (YZ) is ............ bond.
(a-ionic, b- pure covalent, c- polar covalent, d- coordinate)
7-c: polar covalent
8- The hydrogen bond is formed between .................
(a-two hydrogen atom, b-hydrogen atom and another atom of higher electronegativity, c- metal and nonmetal, d- metal and hydrogen)
8-b: hydrogen atom and another atom of higher electronegativity
9- The hydrogen bond is ........... the covalent bond.
(a- equal to, b-longer than, c-shorter than, d- nearly equal)
9-b: longer than
10- The hydrogen bond is .............. the covalent bond.
(stronger than, b-equal in strength to, c- weaker than, d- equal in weakness)
10-c: weaker than
11- The length of an ionic bond equal to the sum of .............
(a- the radii of the metal and nonmetal atoms, b- the radii of the metal and nonmetal ions)
c) the radii of two non meatl inon, d- there is no correct answer
11-b: the radii of the metal and nonmetal ions
12- The length of a pure covalent bond equal to ..............
(a-twice the radius of one atom, b- twice the radius of one ion, c- the radius of each atoms)
12-a: twice the radius of one atom
13- The length of a polar covalent bond equal to ............
(a- sum of the radii of the two atoms, b-sum of the radii of the two ions, c-twice the radius of one atom, d- twice the radius of one ion)
13-a: sum of the radii of the two atoms
14- In SP hybridization, the number of hybridized orbitals that formed are ..................
(a- 2, b- 3, c- 4, d-5)
14-a: 2
15- In 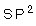 hybridization, the number of hybridized orbitals that formed are ...........
hybridization, the number of hybridized orbitals that formed are ...........
( a- 2, b- 3, c- 4, d- 5)
15-b: 3
16- In  hybridization, the number of hybridized orbitals that formed are ..............
hybridization, the number of hybridized orbitals that formed are ..............
(a- 2, b- 3, c- 4, d-5)
16-c: 4
17- In SP hybridization, the angle between the formed orbitals is ............. 
17-b: 
18- In 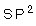 hybridization, the angle between the formed orbitals is .............
hybridization, the angle between the formed orbitals is ............. 
18-a: 
19- In  hybridization, the angle between the formed orbitals is .............
hybridization, the angle between the formed orbitals is ............. 
19-c: 
20- The type of hybridization in methane molecule is .............

20-c: 
21- The type of hybridization in ethylene molecule is .............

21- 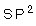
22- The type of hybridization in acetylene molecule is ..................

22-a: SP
23- The ionic bond is formed between two atoms when the difference in electronegativity is ....................
(a- less than 1.7, b- more than 1.7, c- zero, d- less than zero)
23-b: more than 1.7
24- The polar covalent bond is formed between two atoms where the difference in electronegativity is .................
(a- less than 1.7, b- more than 1.7, c- zero, d- less than zero)
24- a: less than 1.7
25- The pure covalente bond is formed between two atoms where the difference in electronegativity is ................
(a- less than 1.7, b- more than 1.7, c- zero, d- less than zero)
25-c: zero
26- In ammonium ion, the nitrogen atom is ..............
(a- acceptor, b- donor, c- positive ion - d- negative ion)
26-b: donor
27- Aluminuim is harder than sodium because of ..............
(alumunium is amphoteric, b- the increased number of free valence electrons in Al, c- aluminium is non-metal, d- the increase of energy level in Al)
27-b: the increased number of free valence electrons in Al.
28- The boiling point of water is high due to ............
(a- polarity of water molecules, b- the hydrogen bonds between water molecules, c- the covalent bonds within the water molecules
28-d (a and b)
II. Mention the scientific expression for each of the following:
1- A bond results between a metal of high electropositivity and a non metal of high electronegativity.
1- ionic bond
2- A bond results between two non metal l atoms have equal electronegativity.
2- Pure covalent bond.
3- A bond results between two different atoms with a difference in electronegativity less than 1.7.
3- Polar covalent bond.
4- A bond results between two atoms, one of them having a lone pair of electrons, while the other atom have a vacant orbital.
4- Coordinate bond.
5- A bond results when the electron cloud of valence electrons are associated together around the positive metal ions.
5- metallic bond.
6- A bond results when a hydrogen atom is located between two atoms of high electronegativity.
6- hydrogen bond.
7- A bond results when an overlap of atomic orbital head to head along one line.
7- sigma bond.
8- A bond results when an overlap of two atomic orbitals side by side betweeen two parallel atomic orbitals.
8- pi bond.
9- The theory which assumes that all elements (except  , Li and Be) tend to reach the octet structure.
, Li and Be) tend to reach the octet structure.
9- electron theory of valency.
10- The ion which produced when a hydrogen ion accepts the lone pair of valence electrons of Nitrogen atom in ammonia molecule.
10- ammonuim ion  .
.
11- The ion which produced when a hydrogen ion accepts the lone pair of valence electrons of Oxygen atom in whater molecule.
11- Hydronlum ion  or hydroxonium ion
or hydroxonium ion
12- The theory which assumes that the covalent bond is formed as a result of the overlap of an atomic orbital of one atom which contains a single electron, with a similar orbital of other atoms.
12- valency bond theory (VBT).
III. Complete the following sentences:
1- NaCl is soluble in water because .............., while ............. and .................. are insoluble in water.
1- it is an ionic compound, oil, fat
2- In case of ammonia molecule, there are ............ type of bonding.
2- one
3- In case of ammonia molecule, the number of ........... bonds are ............ bonds.
3- covalent, 3
4- In case of ammonuim ion, there are .............. types of bonding.
4- two
5- In case of ammonuim chloride molecule, there are ............. types of bonding.
5- three
6- Ammonuim ion has the formula ............, it is formed between ......... and ........ ion through a ............ bond.
6- 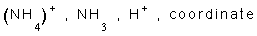
7- Hydronium ion has the formula .............., it is formed between ............... and hydrogen .............. and bond formed is .............. bond.
7- 
8- Methane molecule has a ................ shape, where the angle between the bond are .................
8- tetra Hydral pyramid, 
9- Ethylene molecule has a ............... shape, where the angle between the bonds are .............
9- Planar triangle, 
10- Acetylene molecule has a ................. shape, where the anlge between the bonds are ...............
10- linear, 
11- Sigma bond is .............. than Pi bond.
11-Stronger
12- Magnesium metal is ........... than soduim metal, because the No. of ................. of soduim is ................. than that of magnsium.
12- harder, valence electrons, less.
IV. Give Reasons for:
1- Although the small moleculer weight of water, its boiling point is high.
1- Due to the large polarity between water molecules as a result of the large difference in electronegativity between (O & H) which create hydrogen bonds need high energy to be broken.
2- Noble gases haven't chemical activity.
2- Because the outer most level is saturated and needs no loss or gain of electrons.
3- Aluminium chloride is not considered as an ionic compound.
3- Because the difference in electronegativity between Al & Cl is less than 1.7
4- Acetylene is more reacting than methane.
4- Because acetylene has two week pi bond ready to be broken easily, while the sigma bonds in methane are strong.
5- The octet rule can't be applied to boron trifluoride.
5- Because boron atom is surrounded by 6 electrons (not 8).
6- The octet rule can't be applied to  .
.
6- Because posphorus atom is surrounded by 10 electrons (not 8).
7- Both soduim positive ion and fluoride negative ion hase the same number of electrons.
7- 

 have the same electronic configuration.
have the same electronic configuration.
8- NaCl is soluble in water, but insoluble in or benzene.
8- Because Ionic compounds such as NaCl is soluble in water because water is a polar solvent by which the crystal lattice of salt is broken down while benzene is organic solvents.
V. Compare between each of the following:
1-  and give an example of each.
and give an example of each.

2- Ionic compounds and covalent compounds

3- Sigma bond and Pi bond.

4- Pure covalent bond and polar covalent bond.

5- Covalent bond and coordinate bond.

VI. Put the sign (  ) in front of the correct statments, and (
) in front of the correct statments, and (  in front the wrong ones
in front the wrong ones
1- The melting point of ionic compounds is higher than that of covalent compounds.
1- (  )
)
2- A hydrogen bond is formed between the nitrogen atom of ammonia molecule and the proton (  ).
).
2- (  )
)
3- In ammonia molecule, there are three partial negative charges carried by the nitrogen atom.
3- (  )
)
4- Two atoms of the same electronegativity, combine with a pure covalent bond.
4- (  )
)
5- When the difference in electronegativity is higher than 1.7, an ionic bond is formed.
5- (  )
)
6- When the difference in electronegativity is less than 1.7, a metallic bond is formed.
6- (  )
)
7- The two atoms involved in the formation of the coordinate bond, share in giving the electron pair.
7- (  )
)
8- Coordinate bond should not be formed, unless there are two atoms; one atom donate a lone pair and the other accept it.
8- (  )
)
9- The coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond.
9- (  )
)
10- The metallic bond is a type of covalent bond.
10- (  )
)
TEST 1 ON CH.3:
1 - The polar covalent bond is formed between two atom
less than 1.7
more than 1.7
zero
2 - Two atoms of the same electronegativity, combine
True
False
3 - The length of a pure polar covalent bond equal to
sum of the radii of the two atoms
sum of the radii of the two ions
twice the radius of one atom
4 - Coordinate bond should not be formed, unless there
True
False
5 - The coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond.
True
False
6 - In SP hybridization, the number of hybridized orbi
2
3
4
7 - The bond in HCl molecule is ............... bond
polar covalent
coordinate
pure covalent
8 - The hydrogen bond is ........... the covalent bond
weaker than
stronger than
equal in strongth to
9 - When the difference in electronegativity is less
True
False
10 - The coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond
True
False
11 - The two atoms involved in the formation of the coo
True
False
12 - The length of a pure covalent bond equal to ......
twice the radius of one atom
twice the radius of one ion
the radius of each atoms
13 - In ammonia molecule, there are three partial nega
True
False
14 - In ammonium ion, the nitrogen atom is ...........
donor
acceptor
positive ion
15 - The melting point of ionic compounds is higher tha
True
False
16 - The ionic bond is formed between two atoms when th
more than 1.7
less than 1.7
zero
17 - When the difference in electronegativity is higher
True
False
18 - The metallic bond is a type of covalent bond
True
False
19 - The hydrogen bond is formed between ..............
hydrogen atom and another atom of higher electrone
two hydrogen atom
metal and nonmetal
20 - In SP hybridization, the number of hybridized orbi
2
3
4
QUESTIONS and ANSWERS 2:






















SOLVE BY YOURSELF
















TEST 2 ON CH.2:








Date: 2015-12-17; view: 1372
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| | | THE POWER OF COLOUR |