
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
The organs of speech and their functions
Exercise 1. Fill in the table:
Exercise 2. Answer the following questions about school education in the USA: 1. What are the three levels of governmental control over education in the US? 2. What is the compulsory age of school education in the USA? 3. What is difference between public, private and home schools? 4. How can the school year be organised? 5. What subjects are taught on the primary education level? 6. What subjects are taught on the intermediate level? 7. What are the required subjects on the high-school level? 8. What are the electives? What are the most common types of electives offered by high schools? 9. What are the most common extracurricular activities in US schools? 10. Do the American students have pass a graduation examination?
Exercise 3. What role does the following play in the universities and colleges admission system: l high school transcript l GPA l letter of recommendation l College Entrance Examination Board and American College Testing Program l SAT and ACT l Advanced Placement Program and International Baccalaureate l interview Exercise 4. Characterise the following types of American colleges and universities, name some of the institutions belonging to each group: l The Ivy League l “Public” Universities l Small Liberal Arts Colleges l Technical Institutes l Denominational or Religiously-Affiliated Schools l Community or Junior Colleges Exercise 5. Fill the table with information about university degrees in the USA:
Exercise 6. Answer the following questions about the learning process in American universities: 1. Describe the three systems used to structure the academic year. 2. What is a credit? What are the advantages of the credit-based system of education? 3. What is the difference between graduate and undergraduate study? 4. What learning styles are used in American universities? 5. What is the most widely used system of grading in the US universities? 6. What is the cost of tuition in American universities? 7. What kinds of help can a student receive towards their tuition fees? Exercise 7. Fill in the blanks with the words from the boxes funds loans taxes scholarships student fees federal funds a. Funding. All universities and colleges receive (1)________ from a variety of sources. Private colleges depend primarily on (2)__________ and on endowments and gifts. Public institutions also have these sources, but depend mainly on state and local (3)_________ for operating funds. Both public and private institutions may receive (4)_________for research activities. The federal government distributes aid among colleges and universities according to various formulas based on the number of students who receive (5)_________ and (6)_________, and on the enrollment of graduate students and veterans. board of regents chancellor academic dean president board of trustees b. Management. In most cases, a (7)__________ or (8)__________ is the chief administrator of a university or college. Other officials handle educational programs, registration, management of funds, and collection of tuition. Each college or separate school of a university generally has an (9)___________ or director. He or she leads the faculty in preparing the course of study for the college or school, and takes part in university planning. Most universities and colleges are controlled by a (10)_______________or a (11)______________, which approve educational policies. They also appoint the chief administrative officer of the institution. assistant professors scientists chairman (x2) teachers research fellows departments teaching fellows c. Faculty includes the (12)__________ of a college or university. A college's faculty is divided into (13)___________, each of which deals with one general course of study, such as English, mathematics, or physics. Its head is a (14)__________, who is usually a professor. Under the (15)__________ are other professors, associate professors, (16)______________, and instructors. Some departments also have (17)______________ or (18)_____________. These are graduate students who teach or do research part-time. Some faculties include (19)____________ or other workers whose main activity is research, not teaching. freshman coeducational graduates (x2) junior sophomore senior undergraduates (x2) d. The student body of a university or college is divided into (20)________ and (21)__________. (22)__________ have already received their bachelor's degree and are working more or less independently for a master's or doctor's degree. (23)____________ are studying for their bachelor's degree. The undergraduates belong to one of four classes – (24)_________, (25)_________ , (26)_________, and (27)__________ – according to year of study. Most institutions are (28)__________, with both men and women students. Others admit students of only one sex. Exercise 8. Answer the following questions about teacher training in the US: 1. What types of courses do teacher-training programs include? 2. How does the curriculum of various years of study differ? 3. What documents are required to obtain a teaching job? 4. In what ways can teachers increase their professional level while working?
Self-Assessment
Exercise 1. Answer the following questions. 1. What are the forms that pre-school education in the USA may take? 2. What is the main purpose of elementary school? 3. Schooling in the USA may be organized according to the following patterns: 6+3+3; 6+2+4; 8+4; 6+6. What is the difference? 4. What are the main characteristics of secondary schools in the USA? 5. What are the admission requirements to colleges and universities in the USA? 6. What degrees are offered by institutions of higher education in the USA? 7. What is the difference between colleges and universities? Exercise 2. Explain the meaning of the words in glossary. high school residential college community college graduation gown senior college athletic fee resident tuition credit hour faculty MA/MS thesis junior college vocational school campus-collegiate university tenure full professor undergraduate course an Ivy Leager the Seven Sisters class of 1975 alumnus/alumni sophomore Exercise 3. Fill in the blanks. 1. Keith is an unknown quantity: the results of his oral assessment may be pretty poor but the _________ will certainly praise him for his writing tests. A) invigilators B) associate professors C) teaching assistants D) markers 2. Being a brilliant student, my Mom graduated from Yale with honors.—What were her__________? A) majors B) biases C) affiliations D) in-born abilities 3. Mike’s parents were thrilled to bits about his progress in Spanish. They even traveled to Spain so that their son could master his language code. Right now he has got a good command of five languages. His Italian is a bit ______, though. A) flowery B)rusty C) authentic D) fluent 4. Sheila can still get ____ in Russian, `cause she spent three years in Moscow working at her thesis under professor Dobronravova. A) by B) off C) out D) away 5. We were in the same class and in the same group. That’s why I know perfectly well that he could often bluff his way through without any revision for the exams. –It’s amazing! Could I have a look at your ____ ring? A) wedding B) signet C) engagement D) class 6. My second cousin is not an avid reader, though he passed all his exams in World literature easily and graduated from High School with flying A) colors B) grades C) marks D) performance 7. I haven’t seen the two of my group mates for ages. Last year they were also conspicuously absent at our ____________ event. A) fashion B) sports C) students D) alumni 8. “_______________: principle is of crucial importance if you want to get life tenure. A) “Live or die” B) “Publish-or-perish” C) “Play rough or take your ball and go home” Exercise 4. Fill in the chart with the information needed about the Ivy-League Universities.
Exercise 5. Project work. Prepare the report on the topic: “Higher Education in the USA: pros and cons”.
Further Reading
1. Higher education in the United States: An encyclopedia / [ed. James Forest and Kevin Kinser]. – N.Y. ABC-Clio, 2002. – 831 p.
* 4-H in the United States is a youth organization administered by the Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CSREES) of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) with the mission of “engaging youth to reach their fullest potential while advancing the field of youth development”. The four “H”s stand for Head, Heart, Hands, and Health. ** The standardized evaluation of a student’s grades is called GPA (grade point average). Grades in the United States are generally assigned by a letter: A (highest grade, excellent), B (above average), C (average), D (usually the minimum passing grade), and F (fail). * The terms “college” and “university” are used interchangeably. Differences do exist; a college awards bachelor’s (or undergraduate) degrees mainly, while universities also award master’s and doctoral (or graduate) degrees. Colleges are generally smaller, as well. Larger universities have a wider selection of programs and may be able to provide you with services that a smaller school cannot. * These are Latin honours. * Various plans have been suggested to improve teacher performace. These plans include in-service training (for working teachers); master-teacher programs (where successful experienced teachers work together with the beginners); merit-pay programs (reward teachers with additional pay if their students regularly achieve at higher levels). The organs of speech and their functions
Important organs 1.Lips 2.Teeth 3.Alveolar ridge 4.Tongue 5.Larynx 6. Vocal cords 7. Epiglottis 8. Pharynx 9. Soft palate 10. Uvula 11. Hard palate
Date: 2014-12-29; view: 2119
|
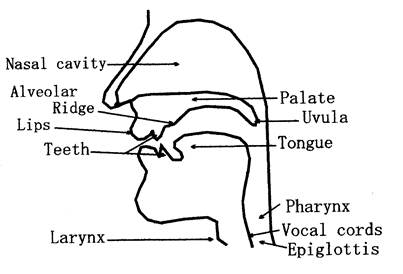 Figure of organs of speech
Figure of organs of speech