
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Replace the words underlined in each sentence with a form of one of the words given. It may be necessary to use a plural or a particular verb form.
Mass, length, time, area, velocity and acceleration all of these quantities are physical ones. Whenever we measure one of these quantities we are finding its magnitude. For example,
30 miles is a measurement of a distance. 30 miles west is a measurement of displacement.
Both have a magnitude of 30 miles. However, the displacement also includes the direction in which it is measured.30 mph is a measurement of speed. 20 mph south-west is a measure-ment of velocity. Both speed and velocity have magnitudes. Which of two has direction (speed or velocity)? 35 mph west is a velocity. 30 miles west is a displacement. Quantities which have magnitude only are scalar quantities, while vector quantities have magnitude and direction.
Mass, volume, area and intervals of time have magnitude only. They are scalar quantities.
Force, velocity and acceleration have magnitude and direction. They are vector quantities.
P. Match each of terms in list A with quantities in list B.
- velocity, speed, displacement, magnitude, direction.
- 30 miles, 30 miles north, 30 min/hr north, 30 min/hr, north.
Q. Which of these magnitudes are scalar or vector?
90 ft / sec north, 47 miles, 15 cm, 14 mph.
R. Fill gaps with the appropriate words.
1. Quantities which are scalar have .. only.
2. Mass, volume, area, intervals of time have magnitude only. They are ..
3. Quantities which have both magnitude and direction are .. quantities.
4. Force, velocity and acceleration have magnitude and .. .They are .
5. The measurement of a scalar quantity consists of . .
6. The measurement of a vector quantity consists of . and .. .
S. Discuss the different systems of measurements, kinematics, scalar and vector quantities,
describe their advantages and disadvantages, prepare a short summary to the lesson 2.
Replace the words underlined in each sentence with a form of one of the words given. It may be necessary to use a plural or a particular verb form.
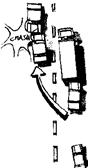
| accelerate ascend endanger reverse collide dismount fasten alight |
a) Ann got off her horse and picked up her riding hat.
b) As the plane went faster down the runway, David began to sweat nervously.
c) Without realising it. Jim drove backwards into a lamp post.............
d) In thick fog. the two ships ran into each other outside the harbour.
e) Passengers who wish to get off at Hove should travel in the front coach.
f) Please do up your safety belt before we begin the journey.
g) The captain refused to put at risk the safety of the crew. ..
h) The balloon rose up gracefully into the summer sky.........
An accident
Read the text and use the context and the diagram to help you with the key words.
There was a serious accident on one of the main roads into Stuttgart this morning. An old lorry (AmEng = truck) broke down in the middle of the road, and the driver couldn't move it. It was eight o'clock, the middle of the rush hour, so it soon created a terrible traffic jam. Drivers got very angry and a man in a Mercedes tried to go round the lorry. Unfortunately another car was coming in the opposite direction. The driver braked hard and tried to stop, but he couldn't prevent the accident - the Mercedes crashed into the front of his car. The driver of the Mercedes was OK, but the other driver was badly injured and both cars were very badly damaged.
Important words and phrases
Taxis (AmEng = cab) use the road; pedestrians use the pavement (AmEng = sidewalk).
The speed limit on motorways in Great Britain is 70 mph (120 kph).
Most petrol stations (AmEng = gas station) in Great Britain are self-service.
Get in the car and remember to fasten your seat belt.
The other car was going very slowly, so I decided to overtake (= pass it on the outside lane).
Vehicles: Study and practice
Try to learn any of the words below that you feel might be useful in a future flying career.
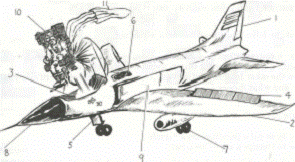 1 tail
1 tail
2 wings
3 cockpit
4 flaps
5 undercarriage
6 window
7 wheels
8 nose
9 fuselage
10 ejector seat
11 parachute
Study the words for the parts of the car illustrated below.
Then test yourself by covering the words and trying to recall them.
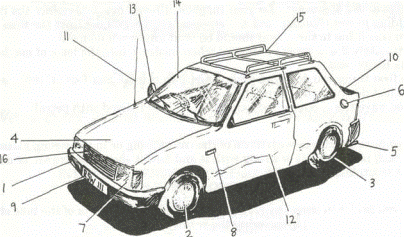 1 bumper
1 bumper
2 wheels
3 tyres
4 bonnet
5 exhaust pipe
6 petrol cap
7 headlights
8 sidelights
9 number plate
10 boot
11 aerial
12 bodywork
13 wing mirror
14 windscreen
15 roof-rack
16 radiator grille
--------------------------------
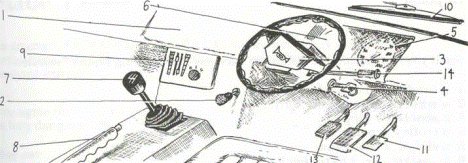 1 dashboard
1 dashboard
2 choke
3 horn
4 ignition
5 speedometer
6 panel
7 gear (stick / lever)
8 handbrake
9 heater
10 windscreen wipers
11 accelerator
12 (foot)brake
13 clutch
14 indicators
Date: 2014-12-28; view: 2756
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| SCALAR VECTOR QUANTITIES | | | Fill each gap in the sentences below with one of the words you see illustrated above. |