
CATEGORIES:
BiologyChemistryConstructionCultureEcologyEconomyElectronicsFinanceGeographyHistoryInformaticsLawMathematicsMechanicsMedicineOtherPedagogyPhilosophyPhysicsPolicyPsychologySociologySportTourism
Break-even point and its role in decision making.
Break-even point (BEP) is the point at which cost or expenses and revenue are equal: there is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even". A profit or a loss has not been made, although opportunity costs have been paid, and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. Economic profits are zero.
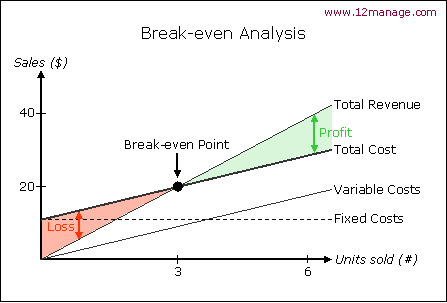
Role: for price-takers it is the test if they may stay in the market. This figure also helps to predict future volumes of incomes depending on the quantity of goods and services produced.
46. External & internal sources of financing.
Internal financing – the company can finance itself with no outside help. The main source – revenues aren’t distributed among shareholders, but retained and used to finance certain activities. Another sources: Amortization (higher volume, more of it is deducted from taxable income), Reserves (Pension for instance), Retained earnings, Asset swaps (selling property or other tangible assets). Main disadvantage: expensive, as internal financing is not tax-deductable. Other disadvantages: no increase in capital, limited volume.
External financing – Debt Markets (bonds, convertible bonds), Equity Markets (IPO, SEO). Disadvantages: shifts in ownership, expensive, no available immediately, estimation of creditworthiness is necessary, information disclosure, risk exposures).
47. Dividend policy and beyond: dividend policy, buybacks, spin-offs.
Dividends are usually paid from net income to a company’s shareholders. Companies don’t distribute all the net income in the form of dividends. A part of it is retained to finance the development of business (retention rate + payout rate = 1). A dividend is allocated as a fixed amount per share. Public companies usually pay dividends on a fixed schedule, but may declare a dividend at any time, sometimes called a special dividend to distinguish it from the fixed schedule dividends.
Form of payment: Cash, Stock, Property or other dividends (structured finance dividends).
Buyback – the situation when company purchases its stocks in order to reduce the number of shares on the market. Companies will buy back shares either to increase the value of shares still available (reducing supply), or to eliminate any threats by shareholders who may be looking for a controlling stake. The company may also want to execute call option if it is “in the money”. Or it has lots of money in cash, so buyback will make the company less attractive for those, who would like to take it over.
Spin-off – the situation when company distributes dividends in form of stocks of a daughter-firm, spun by a parental company. For each of shares of a parent company is given a certain amount of shares in a new venture (usually based on an expected price). Why? 1) to avoid using cash; 2) to develop strengths of a new part of the business; 3) to give more liquidity into that particular part of company and corresponding shares; 4) disagreements between owners; 5) change in legislation.
Date: 2015-02-03; view: 897
| <== previous page | | | next page ==> |
| Income statement and its analysis. | | | Options, futures, forwards, and its applications in corporate finance. |